Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries are the powerhouse behind modern radio-controlled hobbies, drones, and high-performance portable electronics. Renowned for their high discharge rates and lightweight construction, a LiPo batteryoffers unparalleled performance. However, this power comes with a significant responsibility: proper care and handling. While much emphasis is placed on charging correctly, knowing how and when to discharge a LiPo battery is equally critical for its longevity and, more importantly, for your safety.
This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the intricacies of LiPo battery discharge. We will explore the reasons for deliberate discharge, identify the safe voltage thresholds, and provide step-by-step instructions on various discharge methods. Adhering to these guidelines, rooted in expert sources and electrical principles, will ensure you get the most out of your LiPo battery while mitigating risks.
When Do You Need to Discharge a LiPo Battery?
Discharging a LiPo battery isn’t a routine daily task like charging. It’s a specific procedure reserved for particular scenarios. Understanding these situations is the first step in responsible LiPo battery management.
Before Long-Term Storage:This is the most crucial and non-negotiable reason. If you plan not to use a LiPo battery for more than a few days, it must be discharged to a specific “storage voltage.” Storing a battery fully charged or fully depleted accelerates chemical degradation and can lead to permanent capacity loss or swelling.
Disposing of an Old or Damaged Battery:A LiPo battery that is puffed, damaged, holds very little charge, or has reached the end of its life cycle must be discharged to 0V before disposal. This renders it inert and significantly safer to handle and transport to a recycling center.
Balancing Cell Voltage Before a Charge:If you find one cell in your battery pack is significantly out of balance with the others (e.g., after a deep discharge), some experts recommend a slow, controlled discharge to a low voltage to equalize the cells before attempting a balanced charge. This is an advanced procedure and should be approached with caution.
Correcting an Overcharged State (with caution): In the rare event a charger malfunctions and slightly overcharges the battery, a controlled discharge back to the storage voltage can help stabilize it. However, if the overcharge is significant, the battery may be unsafe to handle.
Why is Discharging a LiPo Battery Necessary?
The reasons above are practical, but they are underpinned by fundamental chemical and safety principles.
Preventing Chemical Degradation:A LiPo battery is a delicate electrochemical system. When stored at full charge (4.2V per cell), the internal chemical compounds are under high stress, leading to faster breakdown and the formation of resistive layers on the electrodes. According to research on lithium-ion chemistries (which LiPo is based on), storage at high voltages is one of the primary factors in capacity fade over time (Source: Battery University). Discharging to storage voltage places the battery in a relaxed, stable state.
Ensuring Safety:A fully charged LiPo battery contains a tremendous amount of energy. During long-term storage, the risk of an internal short circuit, while small, never zero. A battery at storage voltage possesses much less energy, making a potential failure—such as a fire or violent venting—far less severe. For disposal, discharging to 0V eliminates the risk of a short circuit causing a fire in the trash or at a recycling facility.
Prolonging Cycle Life:A battery consistently stored correctly will maintain its capacity and performance for many more charge-discharge cycles. By minimizing stress on the internal chemistry, you are directly investing in the long-term health of your LiPo battery.
What is the Safe Discharge Voltage for a LiPo Battery?
This is arguably the most critical technical aspect of LiPo battery handling. Using the wrong voltage can permanently damage your battery.
LiPo cells have a nominal voltage of 3.7V. However, their actual voltage range is much wider. The safe discharge voltage, often called the “Storage Voltage” or “Minimum Safe Voltage,” depends on the context.
Standard LiPo Voltage Chart:
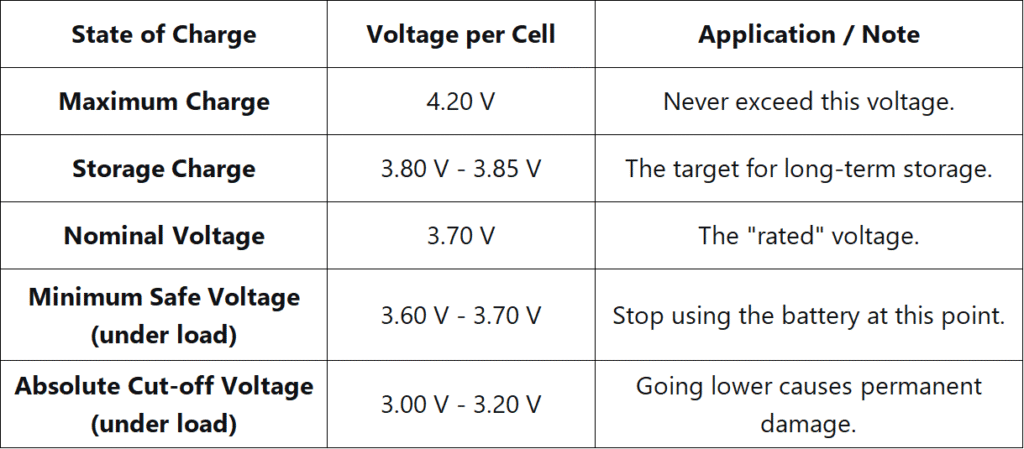
Regardless of whether your LiPo battery’s nominal voltage is 3.6V, 3.7V, or 3.8V, setting the discharge cutoff voltage to 3.2V per cell is a safe, universal, and best practice that effectively extends battery life.

Important Nuances:
Voltage under Load vs. Voltage at Rest:When a LiPo battery is powering a device (e.g., a drone motor), its voltage “sags” under the current draw. The minimum safe voltage under load is typically 3.5V-3.6V per cell. Once you stop drawing current, the voltage will “recover” or bounce back. For a storage discharge, you are targeting the resting voltage of 3.80V-3.85V per cell.
Calculating for Your Pack:To find the voltage for your entire battery pack, multiply the per-cell voltage by the number of cells (S).
2S Pack Storage Voltage:2 × 3.80V = 7.60V
3S Pack Storage Voltage:3 × 3.80V = 11.40V
4S Pack Storage Voltage: 4 × 3.80V = 15.20V
6S Pack Storage Voltage: 6 × 3.80V = 22.80V
Exceeding the minimum voltage during use or discharging a LiPo battery below 3.0V per cell for storage causes “over-discharge.” This leads to copper shunting inside the cell, rendering it unable to hold a charge and creating a significant safety hazard.
How to Safely Discharge a LiPo Battery: Methods and Equipment
Safety is paramount. Always discharge in a safe environment, such on a non-flammable surface like a concrete floor or in a LiPo-safe bag, and never leave the process unattended.
Method 1: Using a Smart Charger/Discharger (Recommended)
This is the safest, most precise, and most convenient method. Most modern AC/DC LiPo battery chargers have a dedicated “Storage” or “Discharge” function.
How it works:The charger uses its internal circuits to dissipate the energy from the battery as heat, often through a large resistor and cooling fan. It carefully monitors each cell’s voltage and stops precisely at the storage voltage (3.85V per cell).
Advantages:Precision, safety, cell balancing during the process, and hands-off operation.
Equipment:A quality balance charger like those from ISDT, HOTA, or SkyRC.
Method 2: Using a Dedicated Discharger Box
These are standalone devices designed solely for discharging LiPo battery packs to storage voltage.
How it works: Similar to a charger’s discharge function, but often at higher power ratings, allowing for faster discharge rates. They are simple to use: plug in the battery and the main discharge lead, set the voltage, and start.
Advantages:Very fast, can handle high capacities, often portable.
Equipment:Brands like iSDT offer discharger boxes compatible with various packs.
Method 3: The Light Bulb Method (DIY)
This is a traditional, low-tech method suitable for users without a smart charger. It requires constant monitoring.
How it works: You connect a light bulb (e.g., a 12V automotive halogen bulb) to the main discharge leads of the LiPo battery. The bulb acts as a resistor, converting electrical energy into light and heat. The battery discharges until its voltage is too low to power the bulb brightly.
Advantages: Inexpensive and effective.
Disadvantages:Imprecise. You must use a multimeter to constantly check the voltage to avoid over-discharging. It does not balance the cells. This method is generally not recommended for high-value batteries.
Method 4: Discharging to 0V for Disposal
For a damaged or end-of-life LiPo battery, the goal is a full discharge to 0V.
The Salt Water Method (Controversial): Submerging the battery in a bucket of salt water is a commonly cited but slow and environmentally questionable method. It can take days to weeks, and the resulting contaminated water must be disposed of as hazardous waste. Many experts now advise against it.
The Light Bulb Method to 0V:The most recommended DIY method. Connect a small, low-power bulb (like a 5W Christmas tree bulb) to the main leads. Let it drain the battery completely until the bulb no longer glows. This can take a long time. Confirm 0V with a multimeter.
Using a Dedicated Discharge/Disposal Device:Some devices are designed to safely discharge batteries to 0V for disposal.
Warning:A LiPo battery discharged to 0V is permanently dead and cannot be recovered. Only do this for disposal purposes.
Step-by-Step Guide to Discharging a LiPo Battery for Storage
Follow these steps for a safe and effective discharge using a smart charger.
- Prepare a Safe Area: Conduct the process on a non-flammable surface in a well-ventilated area. Placing the battery and charger in a LiPo-safe bag is an excellent precaution.
- Inspect the Battery:Visually check your LiPo battery for any damage, punctures, or swelling. If the battery is puffed or damaged, do NOT use a charger. Move to the disposal procedure.
- Connect the Battery: Plug the main discharge lead (e.g., XT60, EC3) into the charger’s discharge port. Then, connect the balance lead to the corresponding port on the charger. This is crucial for monitoring individual cell voltages.
- Select the “Storage” Mode: On your charger, navigate the menu and select the “Storage,” “Store,” or “Discharge to Storage” function.
- Set Parameters:The charger should automatically detect the cell count (S) and chemistry. Confirm these settings. You may need to set the discharge current; a rate of 1C (e.g., 5A for a 5000mAh battery) is generally safe.
- Start the Process and Monitor: Begin the discharge. The charger will display the progress, including individual cell voltages. The process can take a while, especially from a full charge. While modern chargers are safe, it is good practice to check periodically for excessive heat from the battery or charger.
- Verify and Disconnect: Once complete, the charger will beep and display a message like “Storage Complete” or “Done.” Verify that the total voltage and individual cell voltages are in the 3.80V-3.85V range. Safely disconnect the battery.
- Store Properly: Place the fully discharged (to storage voltage) LiPo battery in a non-conductive, fire-proof container or bag and keep it in a cool, dry place.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of discharging a LiPo battery is a fundamental skill for any serious user. It is not merely a technical chore but a critical practice that sits at the intersection of performance, longevity, and safety. By understanding the “when” and “why,” you can make informed decisions. By adhering to the precise voltage guidelines—specifically targeting 3.80V-3.85V per cell for storage—you actively combat chemical degradation. Finally, by employing a safe method, preferably using a modern smart charger, you transform this necessary task from a potential hazard into a simple, routine procedure.
Treat your LiPo battery with the respect its immense power demands. A properly maintained LiPo battery will not only deliver peak performance flight after flight but will also stand as a testament to your commitment to safety and responsible ownership.

